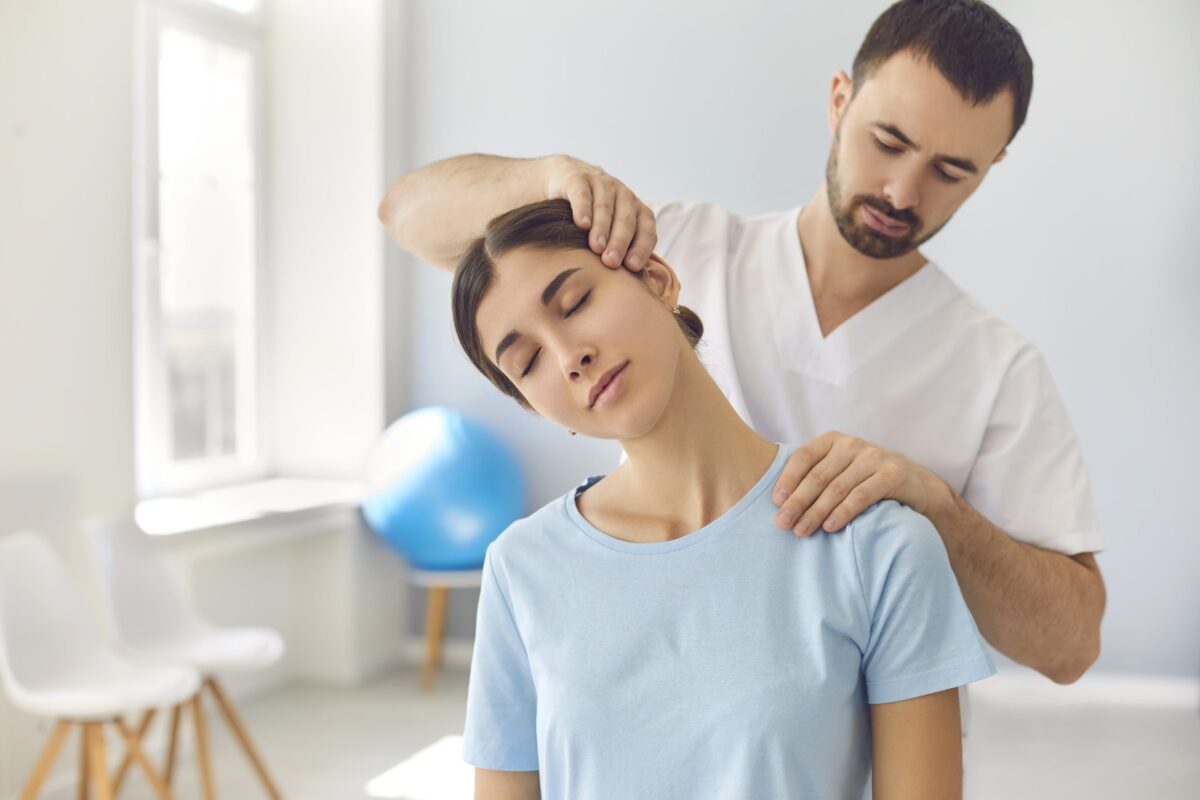
Sciatica is pain that radiates from your lower back down through your legs when your sciatic nerve becomes compressed, inflamed or irritated. This nerve exits the spinal cord at the end of the lumbar spine.
Scoliosis is an abnormal rotation of the spine that can result from developmental abnormalities or severe degeneration. Typical this manifests as a curvature displacing the spine to the side, either to the left or right of midline. Scoliosis can affect both children and adults. Among children, it typically ocurs closer to the age of puberty, and can be associated with symptoms like abnormal appearance of the trunk, difficulty breathing, chest or back pain. In adults, this spinal deformity may cause abnormal posture, back pain and possibly leg symptoms, if pressure on the nerves is involved.
There are many different types of scoliosis. Some of the more common include the following:
Idiopathic Scoliosis – arises from unknown causes. This typically occurs early in life and can progress in around the time of puberty. It can also run in some families.
Neuromuscular Scoliosis – when abnormal curve is attributed to weakening of the musculature that is supporting the spine or improper functioning of the nerves.
Degenerative Scoliosis – occurs in an older population and attributed to the wear-and-tear causing the disc breakdown between each vertebra and arthritis in the facet joints of spinal column.
Congenital Scoliosis – results from problems with the normal growth of the spinal column. It can be associated with the defects in other organ systems.
Scoliosis is easily diagnosed and more easily treated when recognized at a younger age. Treatment can range from simple bracing when it is diagnosed early to surgical correction at more advanced stages. Simple X-ray films can be used to measure the degree of the curve and monitor progression.
Spinal Stenosis occurs when the space around the spinal cord narrows and puts pressure on the cord and spinal nerves. When the disks collapse anddevelops, your body may respond by growing new bone in your facet joints to help support the vertebrae. Over time, this bone overgrowth – called spurs – can lead to a narrowing of the spinal canal. Osteoarthritis can also cause the ligaments that connect vertebrae to thicken, which can narrow the spinal canal.
The most common cause of low back pain in adolescent athletes that can be seen on X-ray is a stress fracture in one of the bones that make up the spinal column. Technically, this condition is called spondylolysis. It usually affects the fifth lumbar vertebra in the lower back and, much less commonly, the fourth lumbar vertebra. If the stress fracture weakens the bone so much that it is unable to maintain its proper position, the vertebra can start to shift out of place. This condition is called spondylolisthesis. If too much slippage occurs, the bones may begin to press on nerves and surgery may be necessary to correct the condition.
Tumors of the spine can be primary or metastatic (spreading from other organs). Symptoms can vary from person to person with most common symptom of pain at the site of the tumor, other can vary from location or size of the mass and include fractures, numbness, loss of bowel or bladder function.
Diagnosis can be made using MRI or Computed Tomography imaging to access the involvement.
Intramedullary tumors – Astrocytomas, Ependymomas and Hemangioblastomas. All arise from cells that compose brain and spinal cord or surrounding blood vessels; located commonly within the covering of the brain and spine. Composed of the soft tissue, does not involve the bone or cartilage.
Extradural tumors – found outside of the spinal cord covering, and is the most common type of spinal cord tumors. Can be malignant or benign and include osteosarcomas, osteoblastomas, and osteoid osteomas. These can involve bone cartilage and other surrounding tissue. Metastases spreading from the lungs, breasts, prostate, and kidneys are more most common cause of above mentioned class of tumors.
Intradural-extramedullary – masses arising in-between the spinal cord and its protective outer covering, include tumors like Schwannomas, and Meningiomas.